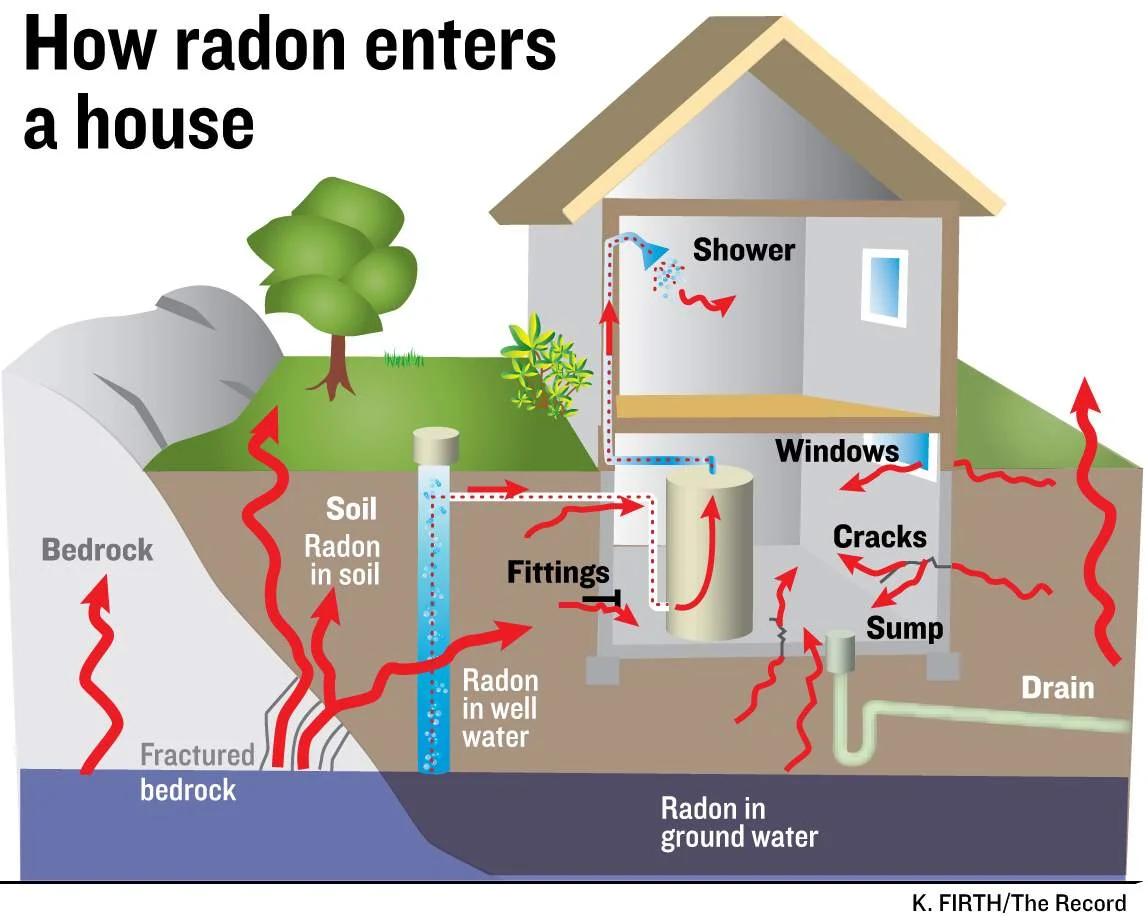
What is Radon?
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as an indirect decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222n, has a half-life of 3.8 days. Radon is one of the densest substances that remains a gas under normal conditions. It is also the only gas under normal conditions that only has radioactive isotopes, and is considered a health hazard due to its radioactivity.
Studies have shown a clear link between breathing high concentrations of radon and incidence of lung cancer. Thus, radon is considered a significant contaminant that affects indoor air quality worldwide. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, radon is the second most frequent cause of lung cancer, after cigarette smoking, causing 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year in the United States. About 2,900 of these deaths occur among people who have never smoked. While radon is the second most frequent cause of lung cancer, it is the number one cause among non-smokers, according to EPA estimates.
(read more at Wikipedia)